What can we really expect from the next console generation?
The future holds more than just prettier pictures

Consoles: The eighth generation
The Wii U's launch marks the transition out of the longest console generation in gaming's history. Yes, even if you think Nintendo is just playing HD catch-up, the Wii U is the beginning of the eighth generation of consoles--Wikipedia says so! Traditionally, the advancement in technology from one generation to the next led to enormous gains in visual quality, which, software aside, was often the marketing focus of any console. Advertisements would scream "look how great the pictures look on this thing!" and kids would point, jaws unhinged, and proclaim how "real" pixelated water was.
So we got to thinking: What can we really expect from games a few years down the road? Surely they'll look better--but will the increase be as dramatic as it had been in generations past? We reached out to the developers of The Witcher 2: Assassins of Kings, one of this generations' biggest eye-pleasers, to talk about next-gen tech and what we might expect hardware advances to bring to gaming in the years ahead.

More realistic lighting
Without proper lighting, there would be no shadows. Everything in the environment--characters included--would be jarringly unconnected. Light is what unites every element to form a single, believable scene in a video game. More processing power would mean more resources for light calculations, which would bolster the life-like presentation of games.
"Our brains have lots of mechanisms to evaluate positions, colors, and other information from the lighting," says Balazs Torok, senior programmer of The Witcher 2. Just as important are shaders, says Krzysztof Krzycin, lead technical artist of The Witcher 2, "a material that defines how the light bounces from an object. With more power, shaders can be more accurate and greatly enhance game realism."

Better character acting
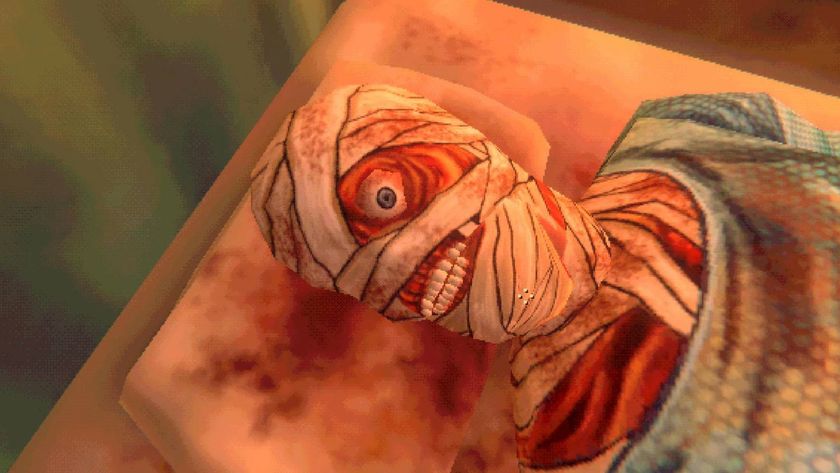
Motion capture tech has advanced pretty dramatically during the past few years alone--just look at the insanity-fueled gestures of Far Cry 3's Vaas, or the facial animations in L.A. Noire. "What current gen games lack in terms of realism is the face mimic," Krzycin says. "Human faces have over 50 muscles that are constantly working and interacting with each other--and most of the interactions are so subtle only a human eye can capture them. With more processing power, new physics-based muscle solvers would greatly enhance in-game characters."
It would be pretty wild if every game had even more advanced facial animations than L.A. Noire--if we could read actual human emotion from the faces of virtual human characters as if they were standing before us. Sure, this might rocket gamers straight into the heart of the uncanny valley, but it could also transform video games into the most emotionally engaging medium of entertainment.

Improved character modeling
This generation introduced a lot of incredibly detailed characters. From Master Chief's upgraded look in Halo 4 to Geralt in The Witcher 2, elaborate character models have pushed the boundaries of what we'd thought possible, especially when we compare games circa 2006 to the games of 2011 and beyond. We know games can create scripted cinematic sequences that are nearly photorealistic--but imagine if characters were that detailed even during gameplay.
"There are powerful tools that let you model a character to the very details of wrinkles, pores, and even the smallest strands of fur on the body, but the time consumed by such a process is not affordable for games," Torok says, citing budget constraints as a hindrance. But still--as technology and modeling techniques continue to develop, perhaps costs will be reduced (and processing power increased) to the point where this becomes reality.

Fancier particle effects
Ever see an explosion occur in a game and watch the fire taper off as smoke billowed into the air? All of that is made possible by particles--essentially small sprites used to mimic real-life events (like explosions) that are difficult to replicate in games. Particle effects have already reached pretty astonishing levels of realism--they're used pretty liberally in most first-person shooters, and often in racing games when cars emit exhaust or kick up dust. But if you think those kinds of things look nice now, think about how they might appear with more processing power available to render them.
"We can display millions of particles," Krzycin says. "The problem is that to light them and make them cast shadows--or to make them physically accurate, interacting with all game objects and with themselves--all that is computationally expensive." He suggests future hardware might allow these effects to be rendered in real time, or allow for more advanced particle simulations. It would be pretty awesome to watch a building get destroyed in a Battlefield game while every rock and bit of rubble collides and interacts in a realistic manner instead of falling apart in scripted chunks.

Smarter artificial intelligence
It's easy to poke fun at NPC/enemy AI in games when those characters are walking into walls or can't navigate a virtual space. Unfortunately, coding believable AI is not quite as simple--after all, this is something we still see pretty frequently in sci-fi fiction. How, then, can we demand perfect AI in video games? "In some ways AI is the final frontier," Torok says. "If we can create believable AI then we can wrap it up even in current-gen solutions--and it would still be amazing."
But could more powerful hardware open the gateway for new scripting routines or processes to be discovered? Perhaps. Not only do computer-controlled characters have to know how or when to interact with players--whose inputs change from person to person--but must also how to navigate a world. As games continue to evolve, so will AI routines, as will the hardware resources required to power them.

Large-scale battles
This isn't to say we haven't seen massive battles done in games before. Dynasty Warriors and the Total War series are obvious examples to the contrary. But what if games could simulate huge, large-scale skirmishes in believable ways? a Dynasty Warriors where you're engaged in a war with hundreds of characters on-screen without any of them feeling like mindless meatbags whose sole purpose is to get killed by your blade?
"Rendering huge amounts of characters is one thing, but making their behavior plausible and realistic is the other thing," Krzycin says. Torok agrees: "Even if we would be able to create all the assets necessary, and there were no limitations in memory or processing power, we would fall back to the problem of having characters aware of their environment and behave properly." So, yeah, we might see more games with more actors on-screen, which is still pretty cool. As for the whole "believable" bit? That's probably a long ways off.

No more loading times
When compact discs became the de facto storage medium for video games, we gradually accepted "Loading..." as a minor inconvenience that would remain with us indefinitely. But it didnt take long for some games to start experimenting with ways to push that annoyance back into the abyss from whence it came.
We've seen this successfully attempted in Max Payne 3, where the loading of level assets occurred under the hood while cutscenes played. Sure, watching these isn't quite as fun as slo-mo diving through giant panes of glass while gunning down bad guys mid jump, but it is more fun than watching a static screen with Dont forget to pop pills if youre low on health! that completely breaks immersion.

More believable worlds
There are few things more frustrating when exploring a giant, open world game than watching trees, shrubs, and buildings suddenly appear as if teleported from some invisible realm. But storing the amount of textures and level data necessary to prevent this would require a lot of memory (which next gen consoles will have more of). "I can imagine the next [console] generation will have much more memory, and hopefully [texture] pops will be gone for good," Krzycin says.
World building techniques such a procedural generation--where game environments are randomly generated on-the-fly by an algorithm (think Diablo II or Terraria)--help prevent the strains of loading a bunch of pre-designed environments into a console's memory. But they don't erase those strains entirely. Krzycin, however, has a concern beyond that of hardware limitations: "Even if you manage to build huge terrain to walk onto, you have to create interesting content--like quests, communities, stories--so the world would not be boring and empty." Yeah, that's kind of important, too.
More user-friendly interfaces
Okay, so the Wii U hasn't exactly been successful with this one, at least in terms of online--but we'll give Nintendo a temporary pass if only because this is one of its first attempts at havingan online interface. Microsoft and Sony, however, have about seven years of experience under their belts. Both have made impressive strides in modernizing their UIs over the past six years, but new hardware will present the opportunity to redesign those UIs without any concessions.
We're also hoping for overhauls in the online front. From joining friends in-game to finding, downloading, and installing apps and games, we're hoping Sony and Microsoft find easier, faster ways for us to quickly find the content we want--and even content we didn't know we wanted. While we're at it, let's make cross-game party chat a mandatory feature, eh?

The gamescape of the future
Yes, the next console generation will bring bigger explosions, more believable AI, and better image quality--but the big leap from this cycle to the next will be in the subtle ways those virtual worlds of the future become more believable. What are you hoping to see in games a few years down the line? Let us know in the comments below.
For more next gen console info, check out our PS4 rumors roundup and Xbox 720 rumors roundup.

Ryan was once the Executive Editor of GamesRadar, before moving into the world of games development. He worked as a Brand Manager at EA, and then at Bethesda Softworks, before moving to 2K. He briefly went back to EA and is now the Director of Global Marketing Strategy at 2K.
Most Popular